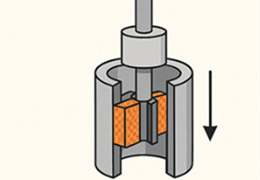
Transverse turning:
+ Larger transverse feed can be realized, that is, larger chip cross-sectional area.
+ High feed rate can be achieved in rough machining.
+ Perfect chip discharge effect.
- Not all profiles can be transversely turned with a limited number of tools, and more tools may need to be replaced during machining.
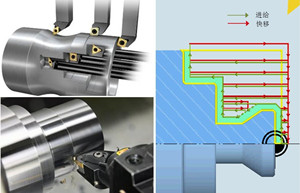 Longitudinal turning:
Longitudinal turning:
+ Avoid empty cutting stroke.
+ Reduced tool changing operation.
+ A high degree of flexibility in applications.
- Not all profiles can be machined due to tool limitations.
- Chip discharge is sometimes less than ideal (chips may become stuck).
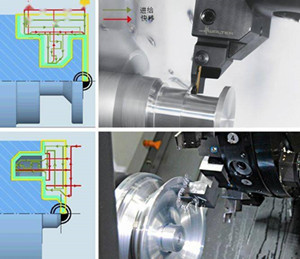 When to use longitudinal turning and when to use transverse turning?
When to use longitudinal turning and when to use transverse turning?
Longitudinal turning is generally used for machining parts with deep grooves and 90° corner structures, which can only be machined by this process.
Transverse turning is generally used for streamlined profile structures with arc transitions.