Electric vehicles have a wide range of components and parts, and the main workpieces include:
.jpg)
1. Electric motor:
The motor is the heart of an electric vehicle, and it is responsible for converting electrical energy into mechanical energy to power the vehicle's wheels.
2. Battery:
Electric vehicles rely on high-capacity batteries to store the electrical energy needed to power the vehicle. These batteries are one of the most critical components of electric vehicles.
3. Power electronics:
Power electronics are responsible for controlling the flow of electrical energy between the battery, motor, and other components. They include components like inverters, converters, and chargers.
4. Transmission and drivetrain:
Electric vehicles typically have a simple transmission and drivetrain, as the electric motor provides high torque across a wide speed range.
5. Chassis and body components:
Like traditional vehicles, electric cars have a range of chassis and body components, including suspension systems, brakes, steering systems, and frames.
6. Heat management systems:
To maintain optimal performance and prolong the lifespan of the electric vehicle components, thermal management systems are necessary. They help to dissipate heat generated by the battery, motor, and other components.
7. Charging system:
Electric vehicles require a charging system to recharge their batteries. These systems can vary widely, from standard wall outlets to high-speed charging stations.
8. Regenerative braking system:
Most electric vehicles use a regenerative braking system, which recovers energy that would otherwise be lost during braking and uses it to recharge the battery.
9. Tires:
Electric vehicles require tires that are optimized for efficiency and electric drivetrains. These tires often have low rolling resistance to maximize range and reduce energy consumption.
10. Electrical wiring and connectors:
Electric vehicles have a complex network of sensors, wires, and connectors that allow the various components to communicate and interact with one another.
11. Electronics and control systems:
Electric vehicles use a range of control systems and sensors to monitor and optimize performance, including systems that manage battery charging, motor control, and regenerative braking.
12. Interior components: Electric vehicles have a range of interior components, including seats, dashboard controls, infotainment systems, and climate control systems.
As you can see, electric vehicles have many different workpieces that must work together seamlessly to deliver an efficient, reliable, and high-performance vehicle.
Technological changes brought about by hybrid and electric vehicles:
► Higher motor speed for electric drive systems
► Higher precision requirements for gearbox gears and gear shafts
► Fewer gears in the gearbox and relatively shorter driveshaft length
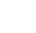
Grinding Solutions for Electric Vehicle (EV) Drivetrain System:
Electrifying the powertrain of vehicles enables locally emission-free mobility and an exhilarating driving experience. However, to achieve long driving ranges, a significant amount of energy is required if relying solely on the electric motor for propulsion. Fortunately, by optimizing motor efficiency in the drivetrain, an increase in range or a reduction in battery capacity is possible. Ensuring the safe operation and extending the lifespan of the battery is accomplished by Battery Management Systems, which monitor and control all battery-related processes, such as charging, discharging, and cell balancing. Additionally, brake energy can be converted into electrical energy and stored. Thanks to the immediate availability of full torque, purely electric propulsion delivers enhanced performance right from the start.
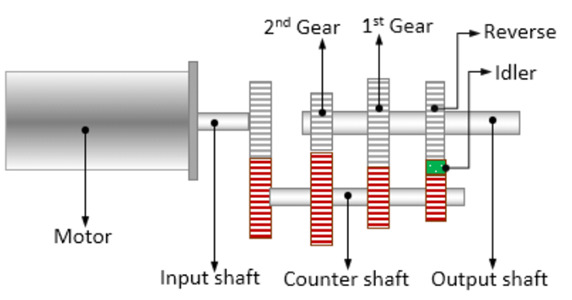
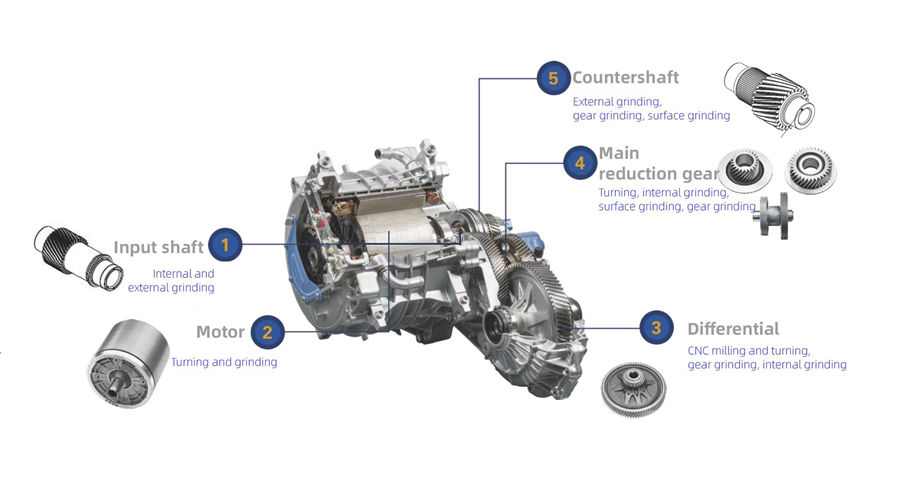
 Moresuperhard Grinding Solutions for Input/Counter/Output Shaft:
Moresuperhard Grinding Solutions for Input/Counter/Output Shaft:

 External/Cylindrical Profile Grinding:
External/Cylindrical Profile Grinding:

 Moresuperhard Excellent Star Products:
Moresuperhard Excellent Star Products:
Moresuperhard Vitrified and Resin CBN Grinding Wheels for Precision Surface Polishing:
► Application: grinding
crankshaft/motor shaft/input shaft/counter shaft/output shaft
► Model : 1A1 CBN wheel
►
Wheel speed is generally 80m/s-120m/s
Moresuperhard Resin Centerless Grinding Wheels:
.jpg)
.jpg)
► Application: grinding carbide, ceramic, magnetic materials, stainless steel bar, PCD & PCBN compositives
► Model: 1A1 , 6A1, 9A1
► Bonded Type: Resin bond, Metal bond
► Centerless Grinder Machine: Koyo, Crystec, Dedtru, Landis , Okuma, Paragon, Royal Master, Unison, WMV
SG Grinding Wheels for Gear Industry:


► Aluminum oxide grinding wheel
► 5-10 Times than the grinding wheel made of common corundum
► Very good cutting capability, sharp grains
Internal Grinding:
Moresuperhard Internal Vitrified/Resin CBN Grinding Wheels:



Vitrified/Resin bond diamond mounted points are excellent tools for grinding small areas with diamond smoothing tools for making a clear polished surface finish. This tool has a unique quality that is recommendable for stone carving, cleaning up work, glass, ceramic, and metal.
Moresuperhard CBN Honing Stone/Honing Stick/Honing Reamer:

 ► Bonded
► Bonded: metal bond
► Materials of workpiece: carbide,glass and ceramic,cast iron,alloy steel, tool steel, die steel, hardened steel copper, aluminum alloy and other abrasive resistant materials
► Applicable areas: fine grinding engine pump body, hydraulic cylinder bore, hydraulic pump inner bore, cylinder block, valve,oil cylinder nozzle, the inner surface of the spline bore and cylinder hole and blind hole of other series.

.jpg)
.jpg)







.jpg)
.jpg)